Research funding impacts on startups are profound, shaping the landscape of innovation in the U.S. economy. The recent federal funding freeze has created uncertainty for many startups that rely on biomedical and scientific grants, potentially stifling entrepreneurship at institutions like Harvard. As research universities function as incubators for fledgling companies, a lack of funding could hamper the transition from ideas in the lab to market-ready technologies. This disruption not only threatens individual ventures but could also hinder overall economic growth from research, crucial in fostering the startup ecosystem. Without adequate support, the vibrant network of entrepreneurs may face stagnation, undermining decades of progress in scientific innovation.
The implications of research financing on emerging tech companies are far-reaching, particularly in an environment marked by funding uncertainties. When federal backing for scientific endeavors is put on hold, the ramifications extend beyond immediate funding cuts, affecting the very fabric of entrepreneurial growth at prestigious institutions like Harvard. Research universities serve as breeding grounds for innovative startups; thus, hindrances in funding directly influence the startup ecosystem’s ability to flourish. As students and faculty collaborate to bring novel solutions to market, the cessation of grants could stall this entrepreneurial momentum. It’s essential to recognize that scientific funding plays a pivotal role in empowering a cycle of innovation and economic advancement.
The Impact of Federal Funding on Startup Ecosystems
Federal funding plays a pivotal role in nurturing the startup ecosystem, particularly in the technology and biomedical sectors. When institutions receive substantial grants for scientific research, they not only enhance their laboratory capabilities but also foster an environment ripe for innovation. For instance, the resources that come from federal funding allow universities like Harvard to invest in state-of-the-art facilities and technology, which can lead to the development of groundbreaking ideas. Such advancements can subsequently be transformed into startups, as faculty and student researchers collaborate to convert academic findings into marketable solutions.
However, when a federal funding freeze occurs, as seen recently in light of political disputes, the implications for startups can be dire. The cessation of financial support stifles the research and development process, delaying the pipeline of innovative ideas that could fuel the next generation of businesses. As startups depend heavily on the preliminary research conducted in these universities, any disruption in funding could result in fewer new ventures emerging, which in turn impacts job creation and economic growth within the broader startup ecosystem.
How Research Funding Influences Entrepreneurship at Harvard
Harvard University stands at the forefront of entrepreneurship, not only due to its rich academic heritage but also because of the support it provides students and faculty through research funding. The curriculum actively promotes the creation of startups, and when federal funding supports scientific explorations, it gives students access to cutting-edge research that shapes their entrepreneurial endeavors. With programs specifically designed to foster innovation, Harvard produces a significant number of startups every year, as students apply their academic knowledge in real-world entrepreneurial efforts.
Moreover, entrepreneurship at Harvard is intricately linked with the availability of funds for research. The more financial resources that are allocated to scientific studies, the higher the probability of groundbreaking discoveries that can become commercial ventures. In the absence of sufficient funding, the entrepreneurial spirit may wane, leading to a decrease in the number of successful startups emerging from the institution. Thus, the network of financial stability for research programs is essential for maintaining Harvard’s reputation as a breeding ground for future innovators.
Economic Growth Driven by Scientific Research Investments
Investment in scientific research catalyzes significant economic growth, a fact supported by extensive studies demonstrating the return on investment for federal funding. For every dollar spent on biomedical research, the U.S. economy sees more than $2.56 in economic activity, showcasing the direct correlation between funding and financial returns. Such investments not only drive new startup creation but also create high-skilled jobs, enhance productivity, and boost overall economic stability.
However, economic growth from research funding is jeopardized by funding freezes, which can slow progress and diminish the impact of previous investments. Startups that emerge from well-funded research initiatives contribute to the economy by introducing new technologies and solutions to the market. The delay in funding not only halts the progress of current innovations but also hampers the development of future technologies that could have widespread economic benefits.
Navigating the Challenges of a Federal Funding Freeze
The recent freeze on federal funding presents a myriad of challenges for research institutions and startups alike. Without access to crucial funding, institutions like Harvard face potential hiring freezes and project cancellations that can disrupt ongoing research initiatives. This uncertain environment creates a ripple effect across the startup landscape, where emerging companies depend on research breakthroughs to develop their products and services. As initiatives are halted, the future pipeline of innovative startups is jeopardized, posing a significant threat to the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Moreover, the implications of a funding freeze extend beyond academia and the startup world; they reverberate through the entire economy. In decades past, historical data has shown that a contraction in research funding typically leads to a reduction in new businesses forming, ultimately stifling economic growth. As a result, the present landscape underscores the urgent need for consistent and reliable funding mechanisms that can support entrepreneurial efforts and drive economic recovery.
Fostering Collaboration Between Universities and Startups
Collaboration between universities and startups is essential for fostering innovation and ensuring the translation of research into practical applications. Research institutions serve as incubators for new ideas, and when adequately funded, they can create synergistic partnerships with emerging companies. These collaborations not only benefit the startups by providing them access to rigorous scientific research and expertise but also reinforce the role of research universities as critical players in the innovation ecosystem.
Furthermore, these collaborations contribute to a vibrant entrepreneurial culture, empowering students and faculty to explore entrepreneurial paths. Programs that facilitate these partnerships will need robust federal backing to thrive. By promoting an interconnected model where research outcomes are harnessed to fuel startup growth, universities can help drive the economy forward while also nurturing the next generation of entrepreneurs.
The Future of Entrepreneurship Amid Funding Cuts
As funding cuts loom over research initiatives, the future of entrepreneurship is at a crossroads. Startups that thrive on the cutting-edge research produced by universities may face diminished prospects due to the reduced availability of resources. Consequently, aspiring entrepreneurs might find it increasingly difficult to bring innovative products to market, leading to a potential slowdown in entrepreneurship and innovation. The long-term effects of such funding restrictions are concerning, as they may hinder the growth of new businesses that could significantly impact the economy.
Nevertheless, with strategic efforts to reverse these funding cuts and an emphasis on supporting research initiatives, there is potential for recovery. If universities can regain access to federal funding, they could continue to serve as vital sources of innovation and entrepreneurship. The path forward for startups will depend significantly on the commitment to reinstating and bolstering research funding, paving the way for a new era of creativity and economic development.
Reversing the Trends of Economic Decline in Innovation
To reverse the trends of economic decline resulting from reduced research funding, it is imperative to recognize the fundamental connection between innovation and financial support. Economic analyses have illustrated that a decline in research funding correlates directly with slower economic recovery and less job creation in tech-oriented sectors. Therefore, it is crucial for stakeholders, including policymakers and educational leaders, to advocate for the reinstatement of federal funding aimed at supporting scientific research.
Recognizing that the health of the economy is closely tied to the vitality of research initiatives, collaboration among universities, government agencies, and private sector investors is essential. By emphasizing the importance of research funding for sustaining the startup ecosystem, stakeholders can take proactive measures to advocate for increased investments in scientific research, ultimately ensuring a robust economic future.
The Long-Term Effects of Research Funding on Innovation
Understanding the long-term effects of research funding on innovation adds depth to the conversation surrounding entrepreneurship in the U.S. economy. A sustained commitment to research funding fosters an environment of continual innovation, where ideas can flourish and evolve into successful ventures. An ongoing pipeline of research not only powers startups but also strengthens existing companies by providing access to fresh insights and technological advancements.
Conversely, as we have witnessed with the funding freeze, interruptions can lead to an innovation desert, where fewer ideas make their way from the lab to the marketplace. The long-term consequences of such interruptions could be further stagnation in the startup landscape, reduced competitiveness on the global stage, and even detrimental impacts on overall economic growth. Addressing these challenges requires a robust dialogue focused on the critical importance of sustaining research investment as vital to the health of the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Evolving the Entrepreneurial Landscape Post-Funding Cuts
Post-funding cuts, the landscape of entrepreneurship faces a steep evolution, adjusting to the realities of diminished financial support. Each funding cycle and research grant serves as a cornerstone for the proliferation of startups, and to witness a downturn in funding is to witness a potential setback in innovation. As entrepreneurs grapple with these funding shortages, there may be a shift in focus towards more sustainable business models that harness existing resources instead of relying solely on external funding.
This transformative period could foster a new breed of startups, ones that prioritize resilience and adaptation in the face of financial challenges. Universities that link arms with startups to share resources and expertise may find themselves at the helm of this shift, steering the entrepreneurial world through the complexities of a funding-constrained environment. Ultimately, the evolution of the entrepreneurial landscape will hinge on adaptability and the strategic alliances forged amidst adversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the impacts of federal funding freeze on startups in the ecosystem?
The federal funding freeze significantly hampers startups by stalling innovation and research projects that rely on government grants. Without essential funding, startups that depend on emerging technologies and scientific breakthroughs may experience delays in development, reduced competitive advantage, and a smaller pool of new ventures emerging from research universities.
How does scientific research funding contribute to the startup ecosystem?
Scientific research funding plays a crucial role in the startup ecosystem by providing the necessary resources for innovation. It empowers research institutions to explore new technologies and methodologies, leading to breakthroughs that can be commercialized into successful startups. This funding ultimately fosters entrepreneurship by creating a robust pipeline of ideas and talent.
In what ways can a freeze in research funding affect entrepreneurship at Harvard?
A freeze in research funding can severely impact entrepreneurship at Harvard by limiting access to resources, such as labs and mentorship. This environment, which typically nurtures innovation and startup growth, could face challenges in generating new ideas and technologies for commercialization, leading to fewer entrepreneurial ventures emerging from Harvard’s ecosystem.
What is the relationship between economic growth from research funding and startup success?
Economic growth from research funding is intimately tied to startup success. Every dollar invested in research catalyzes numerous economic activities, often resulting in new companies that drive job creation and innovation. When research funding is abundant, startups can thrive and contribute to overall economic expansion, whereas funding cuts can stifle this growth.
Why is federal funding for scientific research vital for tech and biomedical startups?
Federal funding for scientific research is vital for tech and biomedical startups because it finances crucial experiments and developments that lead to innovative products. This funding enables universities and labs to attract top talent, fostering an environment where promising ideas can evolve into successful commercial enterprises, thus driving economic progress.
What are the expected long-term effects of cuts to research funding on startups?
The long-term effects of cuts to research funding on startups may include fewer innovative companies entering the market, decreased job creation in the tech and biomedical fields, and a decline in the competitive edge of the U.S. in scientific research and development. Startups that emerge during this period may be less robust due to a weakened support network from research institutions.
How does the startup ecosystem respond to disruptions in scientific research funding?
The startup ecosystem typically responds to disruptions in scientific research funding by seeking alternative funding sources, such as private investments or venture capital. However, these alternatives may not fully bridge the gap created by lost federal grants, potentially leading to fewer startups being established and challenges for those that do manage to launch.
Can the damage caused by a federal funding freeze to research impact startups be reversed?
Reversing the damage caused by a federal funding freeze to research impact on startups may be challenging. Recovery could take one to three years since it takes time for new ideas generated in labs to become viable commercial ventures. Stimulating investments and restoring funding mechanisms will be crucial in revitalizing the startup ecosystem.
| Key Points |
|---|
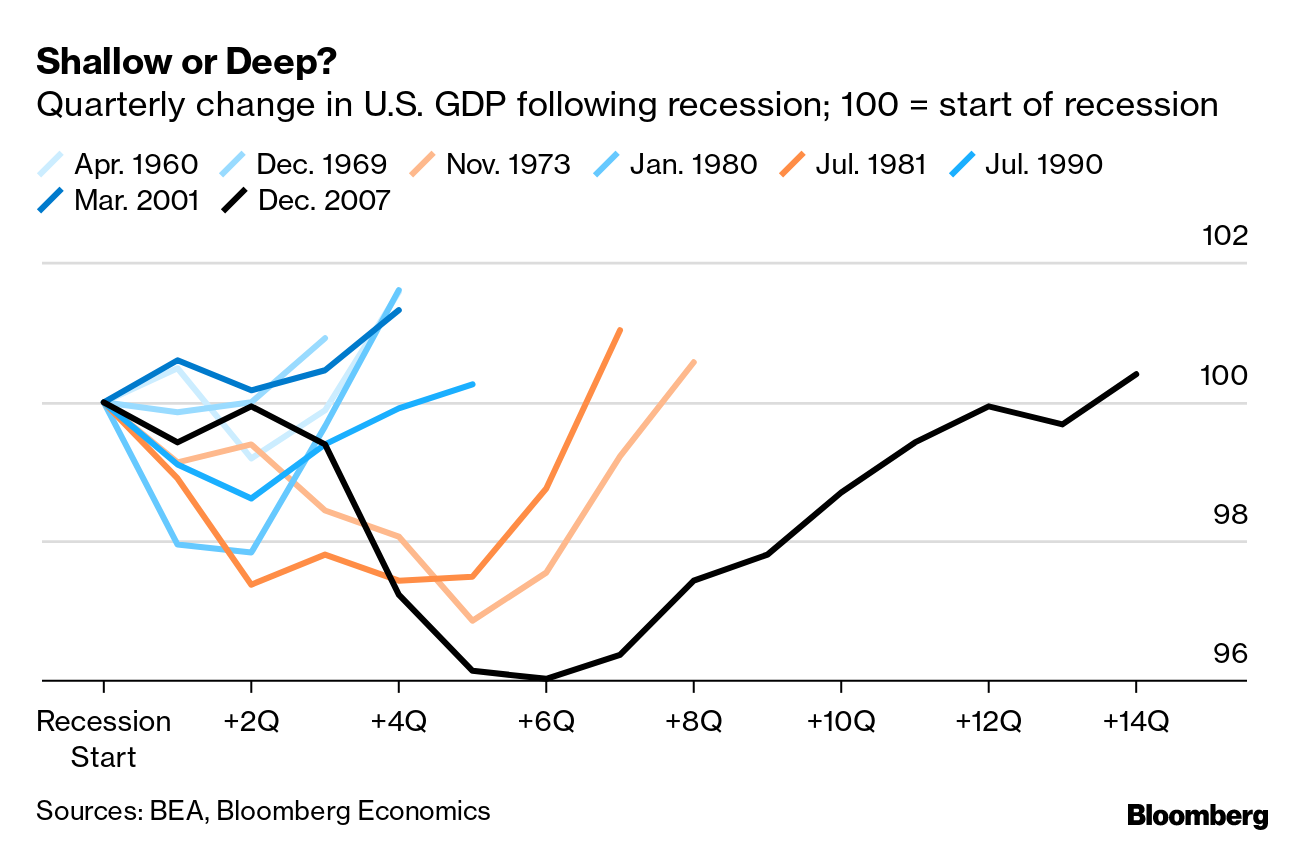
| Federal funding cuts threaten innovation, causing potential economic shrinkage of 3.8% similar to the Great Recession. |
| Research universities act as incubators for startups, fostering entrepreneurship through faculty and student initiatives. |
| Funding influences lab productivity, which directly correlates with the amount of new, successful startups. |
| Short-term effects include hiring and grant freezes, with long-term impacts on startup generation expected in 1-3 years. |
| Loss of research funding could deter aspiring entrepreneurs attracted to top-tier universities. |
Summary
Research funding impacts on startups are profound, as diminishing resources from federal grants can stifle innovation and entrepreneurship. The potential economic fallout from funding cuts threatens not just individual startups but the overall growth of the U.S. economy, particularly as it relates to the critical role research universities play in nurturing new companies. Without sufficient funding, we risk losing a generation of promising startups and weakening the ecosystem that drives technological advancement.