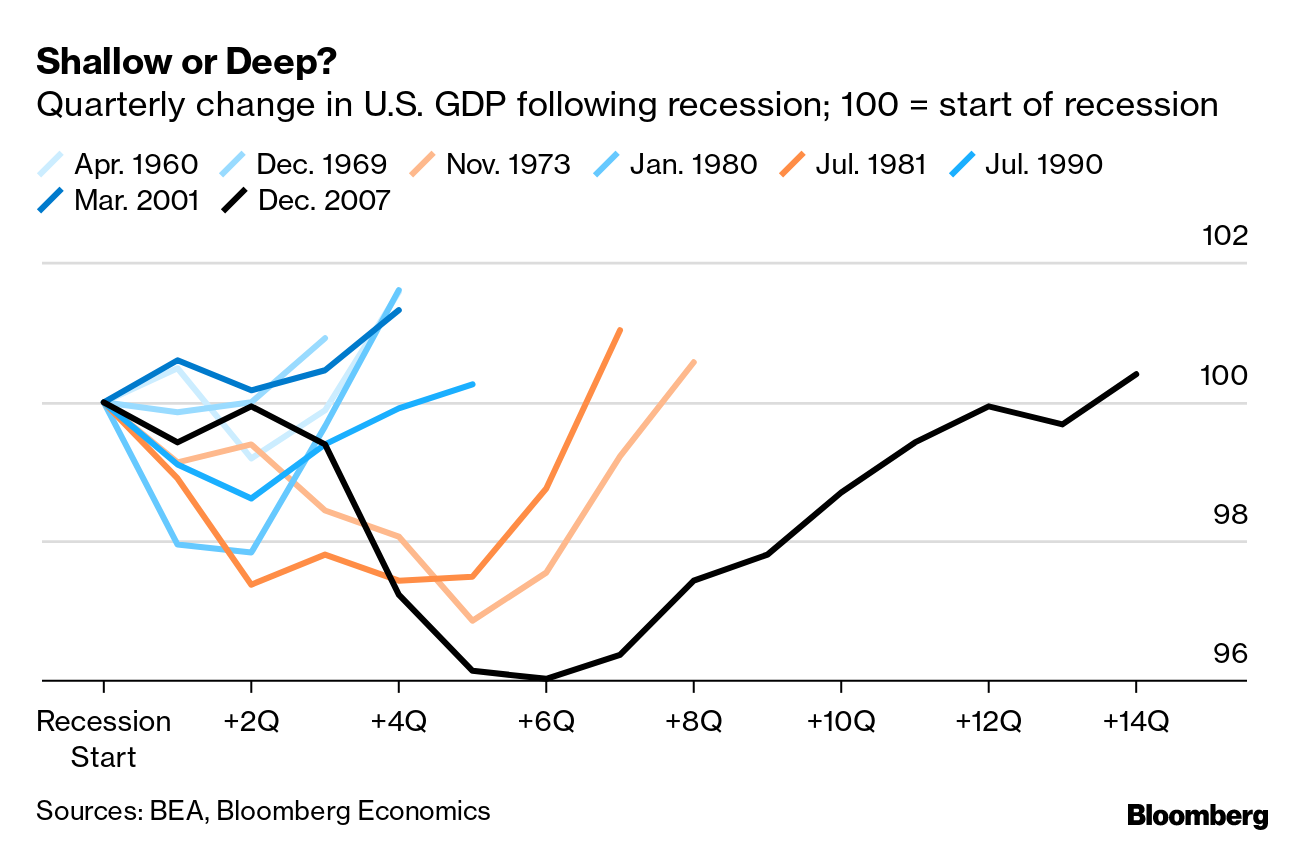
The possibility of a U.S. economy recession looms larger as various factors disrupt financial stability. Recent developments, such as the fallout from the trade war, have contributed to a more volatile stock market, raising concerns amongst investors regarding future growth. Simultaneously, the consumer sentiment index has dipped significantly, reflecting widespread anxiety about economic conditions. With the Federal Reserve weighing its options on interest rates amidst these challenges, the potential for a recession becomes increasingly concerning. The interplay of these elements highlights the economic risks facing the nation and suggests that the road ahead may not be as smooth as hoped.
As analysts assess the trajectory of the nation’s financial health, terms like economic downturn and market instability have emerged to describe the current challenges. Factors such as heightened risk perception, influenced by governmental trade policies, have cast a shadow over investor confidence. Concurrently, fluctuations in consumer sentiment provide a glimpse into the public’s concerns regarding fiscal stability. The looming threat of a recession, characterized by stalled growth and increasing unpredictability, has prompted discussions about appropriate responses from the Federal Reserve. In light of these economic uncertainties, stakeholders are left to navigate a landscape fraught with potential pitfalls.
The Potential for a U.S. Economy Recession
As we analyze the current economic landscape, the looming threat of a recession in the U.S. economy has increasingly become a topic of concern among economists and market analysts. The relationship between various economic indicators, such as the consumer sentiment index and stock market performance, creates a complex narrative that points towards a potentially challenging economic future. With consumers expressing lower confidence and the markets reacting negatively to rising tariffs, many experts predict that a recession may be forthcoming, challenging the nation’s financial stability.
The potential for a recession is not just a matter of speculation; multiple factors contribute to this outlook, including the ongoing trade war with major partners like China and Mexico. As tariffs burden American goods and reduce competitiveness, there is a substantial risk of declining investment and job growth, which are crucial to sustaining economic momentum. Moreover, the increased perception of risk among investors, driven by volatility in economic policy and global trade tensions, further exacerbates the situation, raising the likelihood of an economic downturn.
Understanding the Impact of the Trade War
The ongoing trade war poses significant risks to the U.S. economy, primarily through its influence on investor confidence and consumer behavior. Tariffs imposed on imports not only affect pricing but also lead to trade disputes with key partners, creating uncertainty in the market. This volatility can drive stock prices down and negatively impact economic growth, as businesses may hesitate to invest amid fears of increased costs and retaliatory tariffs from trading partners.
Furthermore, the trade war’s implications extend beyond immediate financial consequences. Long-term damage to international relations can hinder future trade negotiations, affecting various industries reliant on a stable import-export balance. The cumulative effect of these factors can create a challenging environment for economic recovery, as companies tighten their budgets and consumers exhibit hesitation in spending due to the unstable economic climate.
Federal Reserve Interest Rates and Economic Stability
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in navigating the U.S. economy through turbulent financial waters, especially during times of uncertainty such as a potential recession. The central bank faces a delicate balancing act: it must decide whether to lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth or maintain them to control inflation. This dilemma is particularly critical during turbulent periods marked by external shocks, such as the trade war, which can lead to complex economic repercussions.
Interest rate decisions made by the Federal Reserve resonate throughout the economy, influencing consumer borrowing, business investment, and overall economic momentum. A cut in interest rates could offer relief by making borrowing cheaper, potentially boosting spending and investment. However, if inflation remains a concern due to disruption from tariffs and supply chain issues, keeping rates steady might be necessary to prevent further economic instability. This intricate decision-making process highlights the importance of the Federal Reserve’s actions in shaping economic outcomes.
Consumer Sentiment Index: A Reflection of Economic Health
The consumer sentiment index serves as a vital indicator of economic health within the U.S., reflecting the purchasing power and confidence of consumers. As recent reports show a significant decline in this index, the implications are concerning. Lower consumer sentiment typically correlates with reduced spending, which can place additional strain on the economy, especially during turbulent times marked by uncertainty from policies such as tariffs and the ongoing trade war.
Consumer confidence impacts businesses and the overall market significantly, as hesitant consumers may choose to delay purchases or cut back on spending. This cautious behavior can lead to decreased sales revenues for businesses, potentially resulting in layoffs and reduced economic activity. Understanding the dynamics of consumer sentiment is essential for anticipating future economic directions, especially when navigating through risks associated with tariffs and stock market fluctuations.
The Stock Market’s Reaction and Economic Risks
The stock market often serves as a barometer for economic health, reacting swiftly to changes in investor sentiment and broader economic indicators. In light of recent trade war escalations, the U.S. stock market has experienced significant fluctuations, leading many analysts to express alarm at the prospect of a stock market crash. Such downturns can erode wealth, lessen consumer spending power, and perpetuate a cycle of economic decline that may lead to a recession.
These economic risks extend beyond mere financial loss; they can influence global economic relationships and investor confidence in the U.S. economy. Volatile markets can lead to hesitancy among investors and businesses, prompting them to adopt a more cautious approach in their operations and spending plans. As fears of a recession grow, understanding the underlying causes of market volatility becomes increasingly essential for mitigating risks and ensuring stabilizing measures are enacted.
Implications of Government Spending Cuts
Proposed cuts in government spending have raised serious concerns regarding their potential impact on the U.S. economy. Analysts warn that significant reductions could further weaken economic momentum, especially if paired with other risks such as tariffs and external shocks. Government spending plays a critical role in maintaining economic stability, particularly during downturns when businesses and consumers might otherwise tighten their budgets.
Should the government implement drastic spending cuts, it could lead to a contraction in vital public services and investments, adversely impacting economic growth and employment levels. Additionally, such measures may exacerbate public sentiment regarding economic stability, potentially reinforcing fears of a recession, as citizens grapple with the implications of diminished government support during challenging economic times.
Addressing Risk Perception in Investment Decisions
The perception of risk is a pivotal aspect of investment decisions, particularly in times of economic uncertainty. With a landscape characterized by volatile policies and erratic tariff implementations, investors are inclined to adopt a more cautious stance, proceeding with vigilance in their financial strategies. Increased risk perception can deter investments and lead to declines in important economic indicators such as business expansion and consumer spending.
To counteract these dynamics, businesses must cultivate a resilient strategy that accommodates the current economic climate while also preparing for potential recovery post-tariff repercussions. Engaging in transparent communication and employing risk management strategies could help build confidence among investors and consumers, paving the way towards stabilization in an unpredictable marketplace.
Long-Term Economic Predictions Amidst Current Policy Changes
As the economic landscape evolves, predicting long-term outcomes requires careful consideration of current policy changes and external pressures. Tariffs levied during trade disputes have sparked concerns about their lasting effects on the U.S. economy, creating an environment of unpredictability that challenges traditional economic forecasting methods. Analysts argue that thorough assessments are necessary to navigate these complexities and craft sustainable growth strategies for the future.
It is crucial to monitor how ongoing tariffs and government policies shape not just domestic industries but also international relationships. The interplay between economic risks and public sentiment will ultimately drive the market’s performance, influencing everything from consumer spending to employment rates. Therefore, staying informed about these dynamics will be instrumental in preparing for the economic realities of the coming years.
Revisiting Past Economic Crises to Forecast Future Trends
Historical economic crises provide vital insights for analyzing potential future trends, especially in the context of the looming recession warnings faced today. Past downturns, whether driven by stock market crashes, government policy failures, or external shock events, serve as case studies through which economists can draw lessons for current actions. By revisiting the economic landscape of previous decades, we can better understand the precursors to downturns and strategize effectively for mitigating similar events in the future.
Key patterns emerge from past crises, such as the importance of maintaining investor confidence and the pivotal role of consumer sentiment. As we face the complexity of current geopolitical tensions and economic policies, leveraging historical perspectives can empower decision-makers to take proactive steps towards fostering a more stable economic environment, ultimately guiding the nation towards a more resilient future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the U.S. economy recession impact consumer sentiment index?
The U.S. economy recession significantly affects the consumer sentiment index (CSI), which reflects how optimistic or pessimistic consumers are about their financial situation and the overall economy. During a recession, typically characterized by rising unemployment and economic uncertainty, the CSI tends to drop as consumer confidence wanes. Consumers may reduce spending, further exacerbating economic decline, creating a negative feedback loop.
What role do Federal Reserve interest rates play during a U.S. economy recession?
During a U.S. economy recession, the Federal Reserve often adjusts interest rates to stabilize the economy. Lowering interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, which may help spur economic growth. Conversely, if inflation is a concern, the Fed may opt to maintain or increase rates to control it. Thus, the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions are crucial in navigating the challenges posed by a recession.
Can trade wars exacerbate a U.S. economy recession?
Yes, trade wars can exacerbate a U.S. economy recession by increasing costs on imported goods and leading to retaliatory tariffs from other nations. This disrupts trade, raises prices for consumers, and can lead to decreased demand for exports. The resulting economic slowdown can deepen recessionary pressures as businesses face lower profit margins, leading to cuts in labor and investment.
How does a stock market crash signal a potential U.S. economy recession?
A stock market crash often signals a potential U.S. economy recession because it typically reflects declining investor confidence and economic instability. When stock prices plummet, businesses may face reduced capital for investment, leading to cutbacks and job losses. This can decrease consumer spending, triggering a downward spiral that contributes to recessionary conditions.
What economic risks are associated with a U.S. economy recession?
Several economic risks are associated with a U.S. economy recession, including high unemployment rates, decreased consumer spending, and failing businesses. These risks can trigger a chain reaction, leading to reduced investment and confidence, increased bankruptcies, and a possible financial crisis. Moreover, a recession can increase income inequality and strain government resources as safety net demands rise.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Trade War Impacts | Responses from China, Mexico, and Canada to U.S. tariffs have led to market losses and recession fears. |
| Consumer Sentiment | The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index has dropped to its lowest since November 2022, indicating declining economic confidence. |
| Economic Analyst Insights | Economists warn against tariffs, arguing they hurt investment and economic growth rather than help it. |
| Warning Signals for Recession | Analyst identifies increasing risk factors: trade wars, a stock market crash, fiscal crises, and cuts in government spending. |
| Federal Reserve’s Dilemma | The Fed struggles between cutting interest rates to support the economy and maintaining them to control inflation amidst uncertainty. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession is becoming an increasingly pressing concern as recent developments highlight significant risks to economic stability. Analysts warn that the combination of a trade war, decreased consumer sentiment, and erratic government policies has created an environment ripe for recession. With the Federal Reserve caught between the need to stimulate growth and control inflation, the outlook remains uncertain, emphasizing the need for strategic economic policies to avert a downturn.