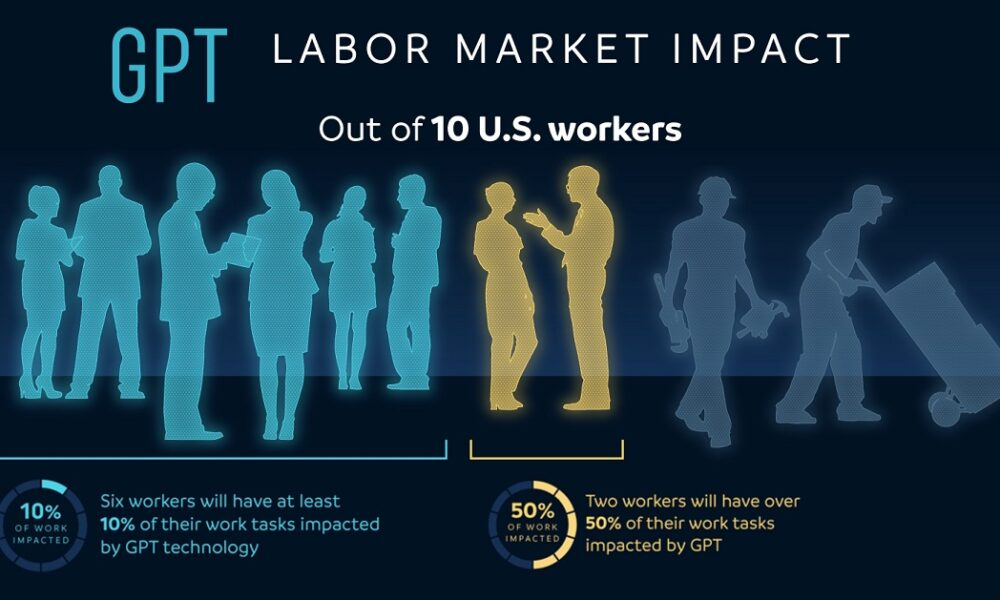
The impact of AI on the labor market is a topic of increasing urgency as we witness technology’s profound influence on employment trends. A recent study highlights how artificial intelligence is driving significant changes, leading to new AI job trends that suggest a transformative phase in workforce dynamics. This shift is accompanied by heightened occupational churn, emphasizing the volatility and adaptation required in various professions. As AI continues to evolve, it raises pressing questions about the future of work and how society will manage these changes in technology and employment. Employers and employees alike must navigate these uncharted waters, adapting to AI workforce changes that could reshape industries fundamentally.
The repercussions of artificial intelligence on employment patterns raise critical considerations for the contemporary workforce. As we delve into how advanced technologies influence job availability and security, it becomes essential to recognize the emergence of trends shaping the job landscape. This discussion encompasses various aspects of labor, from redefined occupations to the skills demanded by an evolving market. Furthermore, the ongoing societal adaptation to such innovations reveals much about our collective approach to work in the future. Navigating these transitions requires a keen understanding of AI’s role as both a catalyst for opportunity and a potential disruptor in traditional job structures.
The Shifting Landscape of AI Job Trends
As artificial intelligence continues to permeate various sectors, it is reshaping the landscape of job opportunities and requirements. One of the most notable trends is the significant increase in demand for roles that necessitate advanced skills, particularly in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). The rise in STEM positions—from 6.5% of the workforce in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024—exemplifies how AI is not merely automating existing jobs but actively creating new specialized roles that require a deeper understanding of technology. This transformation indicates a shift in workforce composition, favoring high-skilled labor that can navigate complex AI systems and leverage data-driven insights to fuel innovation and efficiency in their respective industries.
Moreover, this demand for high-skilled labor correlates directly with trends in AI-driven automation. Occupations that encompass repetitive tasks are experiencing decline, as AI systems particularly excel in these domains. The study’s findings emphasize that the erosion of jobs in low-wage service sectors may not be solely attributed to the pandemic but is part of a long-term trajectory influenced by technological advancements. Individuals seeking employment face a growing divide: while opportunities for highly-skilled jobs inflate, the availability of traditional entry-level roles diminishes, leading to an emerging dichotomy in the workforce that will shape employment for years to come.
Understanding Occupational Churn Amidst AI Advancements
The concept of occupational churn refers to the continuous movement and reshaping of jobs within the labor market, which has been a key focus of researchers examining the impact of technology on employment. As demonstrated in the recent study by Deming and Summers, occupational churn has shown periods of stability and volatility throughout the last century. Notably, the recent increase in churn starting from 2019 aligns with the rapid adoption of AI across various sectors, indicating that AI’s role in transforming employment landscapes is substantial. This churn underscores a significant transition where the skills required for future jobs are rapidly evolving, compelling workers to adapt or risk becoming obsolete in an increasingly automated economy.
Furthermore, the identification of trends such as the end of job polarization reveals that the aftermath of these technological disruptions is influencing not just the quantity of available jobs but also the quality and type. The recent fluctuations indicate that while AI is displacing certain low-skill jobs, it concurrently drives the need for more complex roles that demand higher education and training. As industries invest in AI technologies, career paths are increasingly bifurcated—leading to job growth for those equipped with the right skills while leaving behind those whose work can be efficiently automated. Understanding and adapting to these changes is crucial for both workers and employers aiming to navigate the complexities of the contemporary labor market.
Technology and Employment: A Century of Economic Change
Over the last century, technological advancements have consistently reshaped the American labor market. The study’s historical perspective illustrates how the introduction of groundbreaking technologies—much like the advent of the keyboard or electricity—has led to significant employment shifts. Economists identified eras of both volatility and relative stability, highlighting that while disruptive technologies often lead to fear of job loss, the overall impact may not be as dire depending on the time frame considered. As seen between 1990 and 2017, the labor market experienced low churn, suggesting that technology does not always equate to immediate displacement; instead, it may facilitate adaptation and transition.
However, the researchers caution that the current wave of AI signifies a potential return to volatility. As AI technologies become integrated into the core of business operations, there is an anticipated surge in labor market fluctuations. This includes the decline of traditional roles and the acceleration of a demand for highly skilled workers who can manage and innovate in an AI-driven environment. The research prompts a critical examination of how firms can strategically align their workforce development with ongoing technological changes, ensuring they not only survive but thrive amidst the disruption of the future of work.
The Rise of AI Workforce Changes and Their Impact
The consequences of AI on the workforce are increasingly evident as businesses strive to harness the potential of these technologies. The stark decline in retail sales jobs, which shrank significantly over the past decade, is a prime example of how AI-assisted operations are displacing traditional employment. Companies leveraging AI for inventory management, customer service, and sales analytics have gained competitive advantages, resulting in a dramatic transformation in how goods and services are sold. As the e-commerce sector continues to flourish, it illustrates that while certain jobs are vanishing, new opportunities tied to AI implementation are emerging, albeit requiring different skill sets than before.
Additionally, the growth of AI-driven industries has implications that reach far beyond job loss. The proactive adoption of AI technology fosters an environment ripe for innovation, which can lead to the creation of entirely new sectors within the economy. As industries pivot towards more technologically advanced operations, individuals can no longer rely on traditional employment structures or job security—adaptation is vital. The evolving nature of work necessitates that employees seek continuous learning and reskilling to remain competitive, showcasing how AI-induced workforce changes will likely define the contours of labor in the coming years.
Navigating Future of Work in an AI-Driven Economy
The future of work is undeniably intertwined with advancements in artificial intelligence, prompting a fundamental reevaluation of how businesses operate and how employees engage with their work. As illustrated by the findings of Deming and Summers, the prospects of AI signal significant developments ahead, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its implications on employment structures. Organizations must now strategize their workforce management—emphasizing the importance of investing in training and educational initiatives that align with new demands driven by AI. This proactive approach not only safeguards businesses against the pitfalls of technological displacement but also enhances their competitiveness in a rapidly changing marketplace.
Moreover, the relationship between AI and the future of work emphasizes the necessity for collaborative frameworks among educators, businesses, and policymakers. To maneuver through the potential upheavals posed by AI, it is crucial that stakeholders prioritize workforce readiness and resilience. Ensuring access to skill development resources and fostering an adaptable mindset in workers will help mitigate the risks of unemployment and underemployment associated with automation. As we advance, a collective commitment to understanding and embracing AI’s potential will empower individuals and organizations alike, shaping a more dynamic and inclusive economic future.
Implications of AI on Job Security: A Balancing Act
The integration of AI technologies into the workplace invokes critical questions about job security in various sectors, particularly for roles that may be rendered obsolete. Historically, the fear surrounding job loss due to technological advancements has propelled discussions about job displacement and the need for reskilling. However, the insights from Deming’s research reveal a more nuanced narrative where AI also opens doors for growth in sectors that demand technical expertise. While low-wage jobs may be at risk, those equipped with the skills to work alongside AI can find themselves at the forefront of new job creation—the challenge lies in balancing these divergent outcomes.
Organizations and workers alike must navigate this precarious balancing act by prioritizing worker empowerment and adaptability. As industries evolve with the advent of AI, comprehending the shift toward specialized roles will be central to maintaining job security. Policies that promote skill enhancement and lifelong learning become paramount in equipping employees to thrive amid uncertainties. It is essential that both employers and policymakers actively engage in dialogues that address the complexities of AI-driven labor markets, ultimately fostering an environment where technology serves to enhance job security rather than diminish it.
Future Skillsets: Preparing for an AI-Enhanced Job Market
As we venture into an era dominated by artificial intelligence, the importance of cultivating future skillsets cannot be overstated. The demand for higher education, particularly in STEM fields, is increasingly critical as the nature of job roles evolves. The current trends underline the necessity for individuals to seek educational paths that not only provide foundational knowledge but also encourage the application of technology in practical, real-world scenarios. Skillsets that encompass both technological proficiency and soft skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving will be indispensable. Without these complementary skill sets, workers risk being left behind as the workforce continues to shift.
Moreover, organizations must take on the responsibility of fostering a culture of continuous learning. This includes providing pathways for employee development that bridge the gap between current capabilities and the requirements of an AI-enhanced future. Industry leaders can invest in training programs to improve technical skills and support transitions into new roles, ensuring that the workforce is not just adaptable but also forward-thinking. In doing so, companies not only enhance their operational efficiency but also position themselves as employers of choice in a competitive labor market.
The Role of Economic Policy in Managing AI Disruption
As the U.S. labor market experiences transformations due to AI technologies, the role of economic policy in managing these disruptions is crucial. Policymakers are tasked with creating frameworks that address the shifts in job availability and skill demands prompted by AI’s rise. Effective policies could include investments in workforce development initiatives, support for affected sectors, and incentives for businesses that provide retraining programs for displaced workers. Such strategies will help mitigate potential job losses while fostering industries that are increasingly reliant on technology.
Furthermore, attention must be paid to the promotion of equitable access to educational resources and job opportunities in technology-driven fields. By addressing the disparities in access to training and development, economic policies can ensure that workers from all backgrounds are equipped to thrive in an AI-focused economy. This emphasis on equity not only enriches the workforce but also contributes to a more balanced economic growth, reinforcing the fundamental principles of inclusion and opportunity within the rapidly evolving labor market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current impact of AI on the labor market?
AI is significantly reshaping the labor market by driving trends such as increased job polarization and an uptick in STEM job opportunities. A recent study by economists highlights that AI investments are altering job distributions, contributing to occupational churn, and affecting overall employment stability within various sectors.
How are AI job trends influencing employment patterns?
AI job trends indicate a shift towards high-skilled, well-compensated positions while low-paid service jobs are declining. This reflects a change in the labor market where investments in AI and technology are creating more opportunities in fields like software development and data analysis.
What is occupational churn and how does AI affect it?
Occupational churn refers to the turnover or change in jobs within the labor market. AI is contributing to this phenomenon by automating processes and leading to a decrease in jobs, particularly in low-paid service sectors, while simultaneously increasing demand for skilled labor in technology-related fields.
How does AI influence the future of work?
The future of work is being shaped by AI through the emergence of new job types and the evolution of existing roles. As technology integrates deeper into various sectors, jobs requiring adaptability, technical skill, and innovation are expected to see growth, signaling a shift in workforce requirements.
What role does technology play in employment according to recent studies?
Recent studies, including one by Harvard economists, indicate that technology, particularly AI, plays a pivotal role in employment by creating opportunities in high-skill areas and leading to job declines in more traditional, lower-skilled roles, thereby reshaping the overall job landscape.
Are there specific sectors seeing more AI workforce changes?
Yes, sectors such as retail, STEM, and information technology are experiencing significant AI workforce changes. The rise of e-commerce and predictive AI has reduced the share of retail jobs, while STEM fields are seeing a remarkable increase in job shares, reflecting a shift driven by technological advancements.
What does ‘automation anxiety’ refer to in the context of AI?
Automation anxiety refers to the fear and concern that AI and other technologies will lead to widespread job displacement. Historically, studies have highlighted this anxiety, suggesting that nearly half of U.S. occupations were at risk, but recent data indicates a more nuanced reality with slower rates of disruption until recent years.
How might AI be both empowering and threatening to workers?
AI can empower workers by providing tools that enhance productivity and efficiency, allowing for higher performance. However, it also poses a threat as it can replace certain job functions, leading to displacement of workers who cannot adapt to new technologies or demands in the evolving job market.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization | Shift towards high-compensation jobs; end of downward ramp in wage distribution. |
| Growth of STEM Jobs | Increase of STEM jobs from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, reflecting rising demand for technical talent. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Work | Starting in 2019, a sharp decline in low-paid service jobs contrasting earlier growth trends. |
| Retail Job Reduction | 25% decline in retail jobs from 2013 to 2023, influenced by e-commerce and predictive AI. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly profound as evidenced by recent studies. Research indicates that while past technological disruptions led to occupational churn, the current trends driven by AI are ushering in significant changes, particularly in job polarization, the growth of STEM roles, and a reduction in traditional low-paid labor. Understanding these trends is vital as they shape the future workforce and the types of skills that will be in high demand.