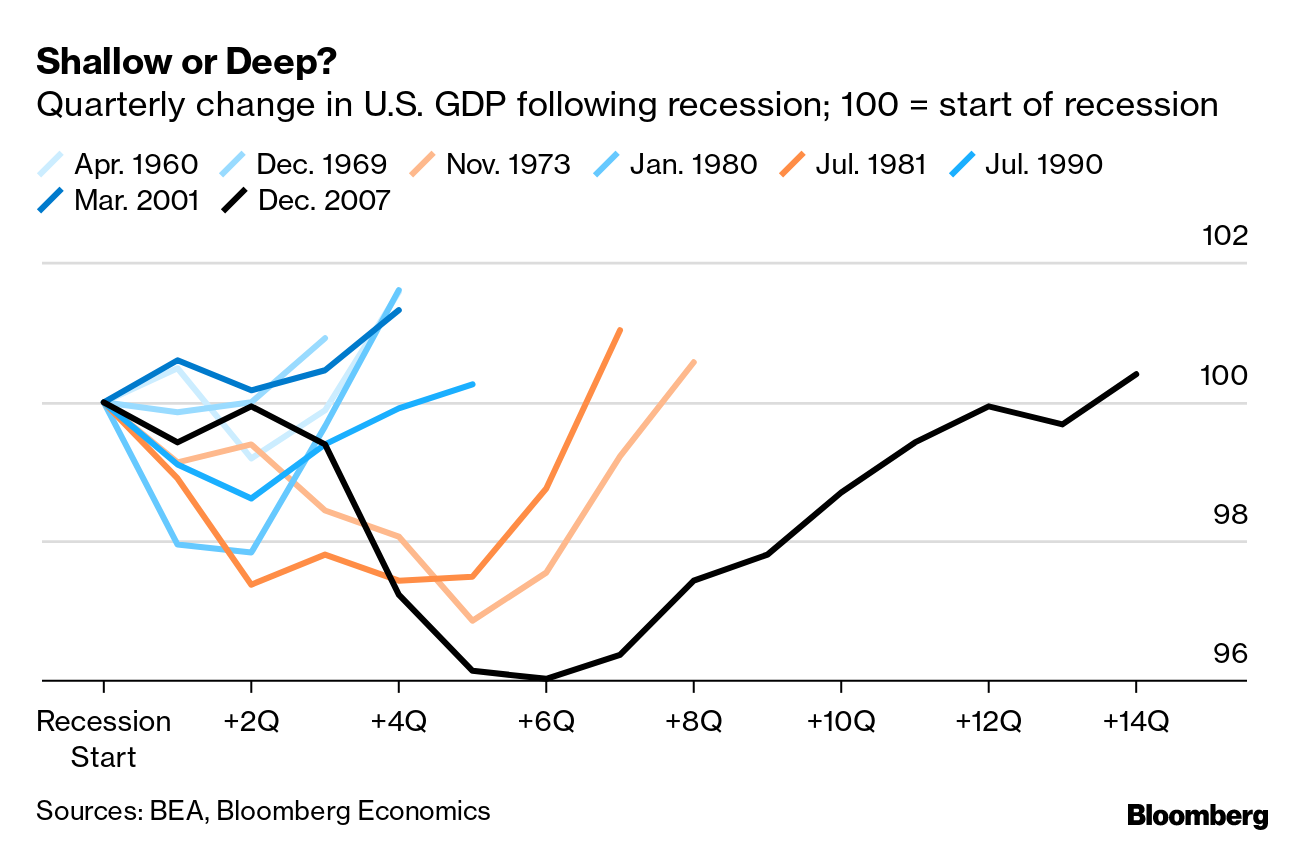
As warnings of a potential recession in the U.S. economy circulate, concerns are mounting regarding the implications of tariffs, market fluctuations, and consumer confidence. The recent downturn in the markets has been exacerbated by retaliatory tariffs imposed by countries like China, Mexico, and Canada, raising fears of an extended trade conflict. In addition, the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index hitting its lowest point since late 2022 suggests a decline in public confidence concerning economic stability. Economists are now closely watching the Federal Reserve’s upcoming decisions on interest rates, which may be crucial in shaping the economic landscape. With recession predictions looming on the horizon, this scenario has implications that could significantly affect both consumers and investors alike.
With recent developments hinting at an economic downturn, the U.S. economy faces mounting inflationary pressures and apprehensions about international trade relations. Analysts are raising alarms about possible recession signals, particularly as the level of consumer sentiment diminishes and stock markets react to tariff-related uncertainties. The role of the Federal Reserve in navigating interest rates is now a focal point of discussion, as shifts in monetary policy could either cushion the economy or exacerbate inflation. As forecasts of economic contraction emerge, it’s essential to explore how these economic indicators influence public perception and investor strategies. The interconnected nature of tariffs, market sentiment, and central bank actions underscores the complex dynamics at play in American economic discourse.
Is the U.S. Economy Headed for a Recession?
Recent economic indicators suggest that the U.S. economy may be teetering on the brink of a recession. Specifically, the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index has plummeted to its lowest point since November 2022, indicating a significant decline in consumer confidence. This is particularly unsettling as consumer spending accounts for a large portion of economic growth. Coupled with ongoing trade tensions, particularly from tariffs imposed by countries like China and Mexico in response to U.S. tariff policies, there’s growing apprehension about the potential for a downturn in the economy.
Economists, including Jeffrey Frankel from Harvard, emphasize the need to closely monitor various factors that could exacerbate the recession risk. These factors include a potential stock market crash, sharp cuts in government spending, and heightened perceptions of overall risk in the market. Tariffs not only disrupt trade but also create uncertainty about future economic performance, causing businesses to hesitate in their investment and hiring decisions. As these concerns mount, both consumers and investors may adopt a wait-and-see approach, further cooling economic activity.
Impact of Tariffs on the U.S. Economy
The imposition of tariffs has far-reaching effects on the U.S. economy, negatively impacting both consumers and businesses. When tariffs are enacted, consumers often face higher prices for imported goods, which can dampen spending. This is especially evident in industries reliant on foreign supply chains, where increased costs may lead to higher retail prices. Such price increases can cause a ripple effect throughout the economy, leading to decreased overall consumer spending and, ultimately, economic slowdown.
Moreover, tariffs can also harm domestic industries by disrupting international supply chains. Rather than fostering growth, tariffs may actually hinder investment and productivity. The trade war initiated by tariff policies has led to general uncertainty in the market, causing some businesses to scale back their expansion plans, which could ultimately detract from job growth and wages. With the Federal Reserve grappling with the implications of these tariffs, it is crucial to consider the long-term effects on economic stability and growth.
The Role of Consumer Sentiment in Economic Predictions
Consumer sentiment is a crucial indicator of economic health, serving as a barometer for future spending behavior. The recent drop in the consumer sentiment index highlights growing concerns among Americans regarding the economy and their financial futures. When individuals feel uncertain, they are less likely to spend money, which can lead to decreased economic activity and growth. This is especially critical in light of current economic conditions where fears of a recession loom large due to rising tariffs and volatile stock markets.
Economists note that a significant decline in consumer sentiment often precedes economic downturns, as it reflects public perception about job security, income stability, and overall economic prospects. If confidence continues to erode, we may see a contraction in consumer spending, which can accelerate the onset of recession. Therefore, it’s essential to monitor shifts in consumer sentiment closely, as it could provide early warnings about broader trends affecting the U.S. economy.
Federal Reserve’s Dilemma: Interest Rates and Economic Stability
The Federal Reserve faces a challenging decision regarding interest rates in the current climate of economic uncertainty. On one hand, lower interest rates can provide much-needed support to the economy by encouraging borrowing and investment. On the other hand, maintaining higher rates is crucial to contain inflation and manage expectations in an environment influenced by rising tariffs and trade tensions. This delicate balancing act complicates the Fed’s strategy, especially as economists anticipate potential recession indicators in the near future.
As the Federal Reserve navigates this dilemma, the risks of raising or lowering interest rates become increasingly pronounced. A rate cut might stimulate short-term economic growth, yet could stoke inflation, while higher rates might curb inflation but simultaneously stifle growth when the economy is already showing signs of weakness. Amid these competing pressures, the Fed’s decisions will significantly impact U.S. economic stability in the months ahead, shaping the trajectory of the economy as it grapples with trade wars and changing consumer behavior.
Analyzing Economic Confidence and Job Market Trends
The interconnection between economic confidence and the job market cannot be overstated. As the consumer sentiment index declines, job growth is also showing signs of slowing, raising concerns about the broader implications for the economy. A lack of confidence among consumers often translates into decreased spending, which can lead employers to halt hiring or consider layoffs, exacerbating economic downturns. With key indicators suggesting a potential recession is on the horizon, tracking hiring trends becomes critical for understanding future economic conditions.
Moreover, the current job market dynamics reveal increasing caution among businesses that may affect employment levels. With many employers opting to adopt a ‘wait and see’ approach in the light of uncertain economic policies, including tariffs, the prospect of a volatile job market increases. Such trends underscore the necessity for decision-makers to implement strategies that can bolster job growth and instill confidence among consumers and investors alike, serving as a buffer against the likelihood of a recession.
Understanding Stock Market Reactions and Economic Forecasts
The stock market serves as both an economic barometer and a source of substantial investor sentiment. Recent fluctuations in stock values, particularly tied to tariff announcements and trade tensions, underline a growing uncertainty that can adversely influence investor confidence. When markets decline, it often causes a cascading effect on consumer and business confidence, leading to decreased spending and investment, which could precipitate an economic downturn.
Analysts and economists alike are closely monitoring stock market reactions as they can provide insight into expectations for future economic performance. If investor sentiment remains pessimistic, it could suggest a lack of faith in economic recovery, eventually affecting real-world economic activities such as consumption and business investments. Consequently, understanding the intricate relationship between stock market performance and economic forecasts is vital for predicting whether the U.S. economy is on the brink of significant challenges.
Future Economic Policies: Strategies for Recovery
As the U.S. grapples with potential recession fears, policymakers are tasked with developing strategies that can promote recovery and economic resilience. Measures such as targeted fiscal policies, infrastructure investments, and support for key sectors could play a significant role in stimulating growth. Additionally, maintaining a dialogue with economic experts and stakeholders is crucial for crafting policies that address current uncertainties while fostering a stable environment.
Moreover, considering the impact of tariffs and global trade dynamics is essential in shaping future economic policies. By focusing on innovation, technology, and competitiveness, the U.S. can potentially offset some of the negative repercussions associated with trade tensions. Ultimately, a multifaceted approach will be necessary to not only safeguard the nation’s economy from the immediate threats of recession but also to harness long-term growth potential in a complex global landscape.
The Importance of Risk Perception in Economic Stability
Risk perception significantly influences economic decision-making, affecting everything from consumer spending habits to investment strategies. As uncertainty reigns due to geopolitical factors, such as tariffs and erratic government policies, overall risk perception among consumers and investors tends to heighten. This increased perception of risk can lead to a more conservative approach in spending and investment, exacerbating economic slowdowns and paving the way for potential recession.
Understanding risk perception and its ramifications on the economy offers valuable insights for stakeholders at all levels. By addressing consumer and investor concerns head-on, policymakers can work to mitigate fears and stabilize economic expectations. Initiatives that promote transparency and predictability in economic policies can help restore confidence, ensuring that the U.S. economy remains on a path toward recovery and growth, despite the looming challenges.
Navigating Tariffs and Trade: The Future of U.S. Exports
The future of U.S. exports is intricately linked to ongoing tariff negotiations and trade policies. As countries retaliate against U.S. tariffs, the competitive landscape for American-made goods alters significantly. Tariffs can serve to protect certain domestic industries in the short term, but they risk isolating U.S. exporters in the long run. This isolation can lead to reduced market opportunities and diminished economic growth as foreign markets become increasingly inaccessible for American products.
To navigate these challenges, U.S. exporters must adapt continuously, developing strategies to mitigate the effects of tariffs, such as seeking out new markets for goods or enhancing product competitiveness. Policymakers face the task of balancing the need for trade protection with the realities of a globalized economy. By fostering open dialogues with trade partners and promoting policies that support export growth, the U.S. can better position itself in an increasingly complex trade environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current U.S. economy recession warnings based on recent economic indicators?
Recent U.S. economy recession warnings stem from a significant decline in the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index, which has dropped to its lowest level since November 2022. Coupled with fears of a prolonged trade war, rising tariffs, and stock market instability, these indicators suggest increasing risk of a recession in the near future.
How do tariffs impact U.S. economy recession predictions?
Tariffs have a negative impact on U.S. economy recession predictions by creating uncertainty in trade relations, which can lead to diminished consumer confidence and investment. The heavy losses in U.S. markets after tariff implementations highlight how these trade tensions can contribute to an economic downturn.
What role does the Federal Reserve play in responding to U.S. economy recession warnings?
The Federal Reserve plays a critical role in responding to U.S. economy recession warnings by adjusting interest rates. In light of current recession risks, the Fed must balance the need to support economic growth with the control of inflation, making decisions about whether to lower rates or leave them unchanged.
How does consumer sentiment index affect the U.S. economy during recession predictions?
The consumer sentiment index is a vital indicator in evaluating U.S. economy recession predictions. A drop in consumer confidence often correlates with reduced spending, which can slow economic growth and exacerbate recession risks as businesses respond by scaling back investment and hiring.
What is the significance of stock market fluctuations in relation to U.S. economy recession warnings?
Stock market fluctuations significantly affect U.S. economy recession warnings, as rapid declines can signal decreased investor confidence and economic instability. A crashing stock market can lead to tightening credit conditions and reduced consumer wealth, heightening recession concerns.
Can increased tariffs lead to long-term effects on the U.S. economy during a recession warning?
Yes, increased tariffs can lead to long-term effects on the U.S. economy during a recession warning by disrupting supply chains, raising consumer prices, and ultimately hindering economic growth. These tariffs contribute to a more unpredictable business environment, making recovery from a recession more difficult.
What are the key factors contributing to recession predictions for the U.S. economy?
Key factors contributing to recession predictions for the U.S. economy include escalating trade tensions and tariffs, declining consumer sentiment, potential government spending cuts, and increased risk perception among investors and consumers. These elements collectively heighten the chances of an economic downturn.
How can economic uncertainties influence U.S. economy recession predictions?
Economic uncertainties significantly influence U.S. economy recession predictions by affecting investment and consumer behavior. When businesses and consumers anticipate instability, they often adopt cautious spending practices, leading to a slowdown that can trigger or exacerbate recession conditions.
What actions can the Federal Reserve take in response to U.S. economy recession warnings?
In response to U.S. economy recession warnings, the Federal Reserve can adjust interest rates, implement quantitative easing, or provide forward guidance to bolster economic confidence. These actions aim to stimulate growth and mitigate recession risks while addressing inflation concerns.
Are there historical examples when the U.S. economy faced a recession due to similar conditions?
Yes, historical examples such as the 2008 financial crisis show how elevated consumer debt, loss of confidence, and government policy changes—including interest rate adjustments—contributed to a significant U.S. recession. Such patterns of uncertainty and economic strain are evident in current recession warnings.
| Key Points |
|---|
| U.S. economy facing potential recession warnings due to trade wars and stock market instability. |
| Federal Reserve is contemplating interest rate cuts amid falling consumer sentiment. |
| Trade policies under the current administration are causing investor uncertainty and market volatility. |
| Historical context with examples like Korea’s debt crises indicates risks of prolonged economic pain. |
| Factors influencing potential recession include trade wars, stock market crashes, and increased risk perception. |
| Uncertainty in economic policy may lead to slower hiring and potentially trigger a recession. |
| The Federal Reserve faces a challenging decision regarding interest rates amid conflicting economic signals. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession warning suggests that the current climate is fraught with potential downturn indicators. Economic uncertainties stemming from trade wars and a volatile stock market raise considerable concerns among economists and investors alike. Moreover, recent declines in the consumer sentiment index reflect waning confidence in the economy’s stability. The Federal Reserve’s response, whether to cut interest rates or maintain them to control inflation, remains crucial in navigating these challenging waters. It is essential for policymakers to address these issues proactively to mitigate the risks of a recession.