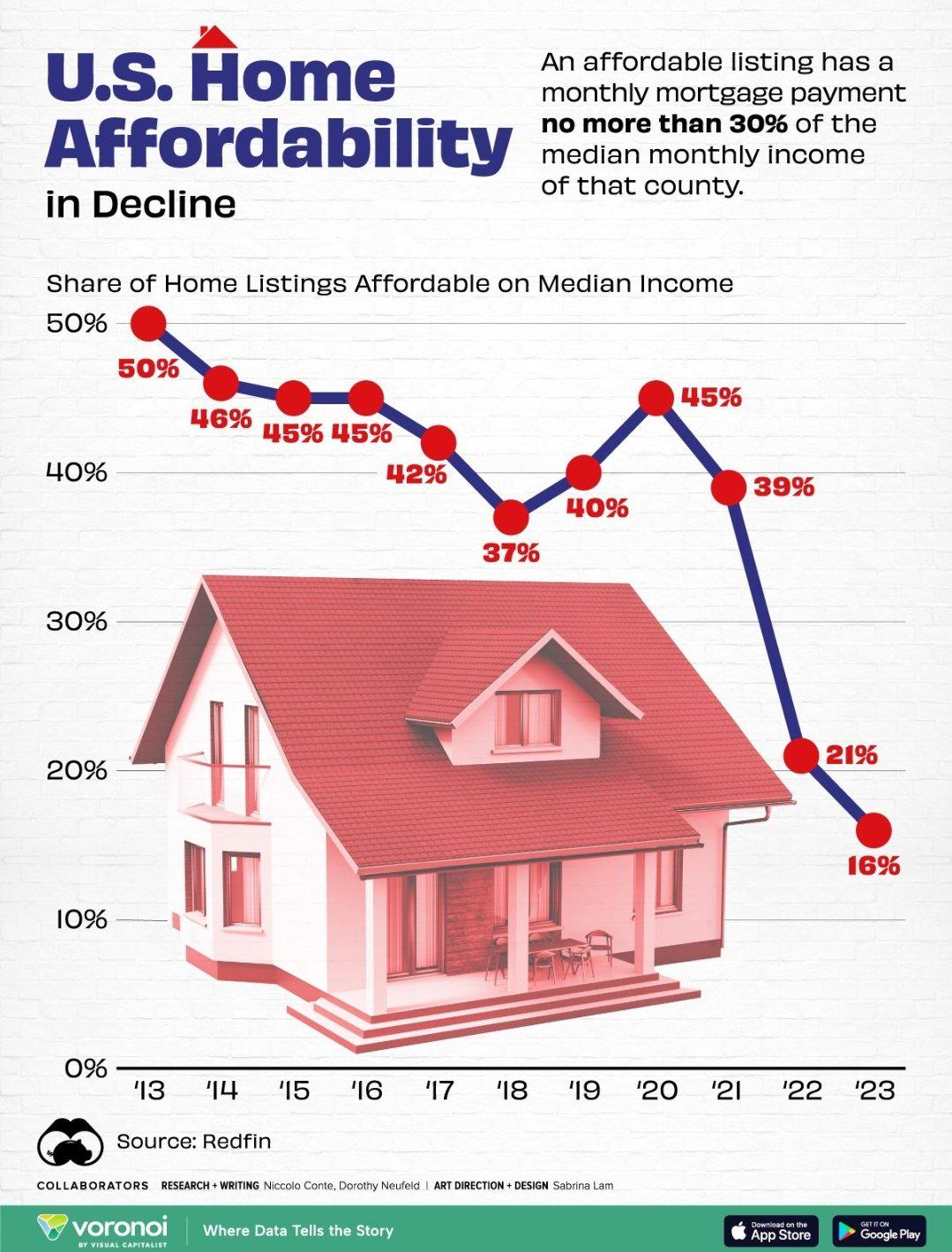
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that continues to challenge many American families today. As home prices soar, fueled by rising labor and material costs, more individuals find themselves locked out of the housing market. Compounding this issue are restrictive land-use regulations and NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies that hinder the construction of affordable homes. These barriers not only restrict the supply of housing but also diminish construction productivity, making it difficult for builders to respond to increasing demand. Consequently, the dream of homeownership is becoming an unattainable goal for a growing number of citizens, highlighting the urgent need for reforms that will facilitate a more accessible and equitable housing landscape.
The challenge of affordable housing has emerged as a significant hurdle for millions of Americans, often described as a housing affordability crisis. This dilemma is characterized by a surge in property costs, making it increasingly difficult for families to achieve homeownership. Often intertwined with stringent land-use policies and NIMBY sentiments, these challenges inhibit construction productivity and limit the availability of diverse housing options. Moreover, the current housing market reflects a trend where innovative building practices are overshadowed by regulations that favor existing homeowners over prospective buyers. As these barriers persist, the conversation surrounding affordable housing solutions becomes more critical than ever.
The Impact of Land-Use Regulations on Housing Affordability
Land-use regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of housing affordability in America. These regulations, designed to manage the growth and development of urban areas, often restrict the supply of new homes by imposing stringent zoning laws and building codes. As evidence suggests, these regulations contribute to the rising costs associated with home construction, making housing less accessible to average Americans. According to recent studies, tighter land-use controls have hampered construction productivity and innovation among builders, affecting the overall supply in the housing market. This stagnation has not only escalated prices but has also widened the gap in homeownership, leaving many families unable to purchase affordable homes.
Moreover, the consequences of NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) attitudes exacerbate this situation. Communities often resist new developments due to concerns about changes in neighborhood character, traffic, or environmental impacts. While these sentiments are understandable, they lead to increased restrictions on new housing projects, which directly impacts construction scalability. Developers find themselves navigating a complex web of regulations that prioritize small, bespoke projects over large-scale developments, stifling innovation and diminishing economies of scale. This cycle perpetuates the housing affordability crisis, as smaller projects yield fewer units, ultimately driving prices higher.
The Detrimental Effects of NIMBY Policies on Builders
NIMBY policies have a severe impact on the construction industry by creating barriers to entry for new housing developments. These policies often manifest in the form of public opposition to local projects, resulting in lengthy approval processes and, in some cases, outright rejection of developments deemed undesirable by residents. Such opposition stunts local economic development, as builders can find it challenging to justify large-scale investments in areas that exhibit strong NIMBY sentiments. Consequently, this environment discourages innovation and competition among builders, further sidestepping the pressing need for more housing.
The decline in housing starts can also be linked to smaller construction firms that emerge in NIMBY-dominated regions. Research indicates that larger firms, which typically have the necessary resources to undertake substantial projects, are diminishing due to regulatory hurdles. As larger firms exit the market, the remaining builders are often ill-equipped to handle the escalating demand for housing, leading to inadequate inventory. This not only hampers construction productivity but also leaves numerous families facing significant homeownership challenges in their search for affordable housing.
Construction Productivity and Its Decline Since the 1970s
A dramatic change has occurred in construction productivity since the 1970s, with the U.S. housing sector exhibiting a significant decline in output per worker. As the economy progressed, the construction industry lagged, revealing that while other manufacturing sectors thrived, housing construction productivity fell drastically. The reasons behind this downtrend are multifaceted, but land-use regulations and smaller project scales are at the forefront. These constraints limit builders’ ability to implement cost-effective production techniques, resulting in increased labor and material costs that ultimately inflate home prices.
In their analysis, economists have found that the era of mass production in housing has all but vanished. Where builders of the past could capitalize on economies of scale to produce thousands of homes efficiently, today’s construction firms are faced with fragmented projects that demand meticulous adherence to diverse local regulations. As productivity declined, so too did the prospect of affordable housing for many Americans. Families seeking homeownership are now confronted with prices that have surged to nearly double those seen in the 1960s, driven in part by these steep reductions in construction efficiency.
Homeownership Challenges Facing the American Dream
The American dream of homeownership is increasingly becoming an elusive goal for many. With soaring home prices and a housing affordability crisis gripping vast swathes of the country, the aspirations of first-time buyers and young families are often crushed under the weight of economic realities. According to studies, millennials and younger generations face significant hurdles in securing affordable housing, primarily due to high costs and limited availability. The burdens imposed by land-use regulations, high construction costs, and the dynamics of the housing market elevate these challenges, making it difficult for many to enter the market.
In addition to financial obstacles, homeownership also carries societal implications. The disparity in home equity between generations highlights a growing divide; younger individuals find it increasingly challenging to build wealth through real estate. Research has indicated that older homeowners have significantly more equity accumulated than their younger counterparts, which creates an intergenerational transfer of wealth that perpetuates economic inequality. Unless there are meaningful reforms to address housing market dynamics, including land-use regulations and construction productivity, the dream of homeownership may remain out of reach for millions.
Innovations in Homebuilding and Market Adaptation
As the housing market continues to grapple with regulatory challenges and rising construction costs, innovations in homebuilding practices are emerging as potential solutions. Advances in technology are reshaping how homes are designed and constructed, enabling builders to optimize processes and reduce costs. Concepts such as modular construction and prefabrication are gaining traction, which can lead to faster build times and enhanced efficiency. Furthermore, integrating sustainable building practices can lower long-term living costs, making homes more affordable over their lifecycle.
Despite these promising developments, they must be embraced within a framework that also addresses the regulatory barriers imposed by NIMBY sentiment and restrictive land-use policies. Policymakers need to create an environment that encourages builders to explore innovative solutions while also fostering collaboration with local communities. By balancing community interests with the urgent need for increased housing supply, the market can adapt to current challenges and work towards making homeownership a reality for more Americans.
The Future of the Housing Market Amidst Economic Pressures
Looking ahead, the housing market will likely face continued pressures from various economic factors coupled with existing regulatory challenges. Inflation, interest rates, and labor shortages all contribute to an uncertain future for homebuyers. As prices remain high, the gap between demand and supply will continue to widen, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis. An essential factor will be how effectively policymakers address land-use regulations and NIMBY attitudes that hinder new developments.
However, with the recognition of these barriers comes the opportunity for reform. By reevaluating policies that have historically restricted housing supply, local governments and communities can play a pivotal role in revamping the housing landscape. Moreover, fostering a culture of innovation within the construction sector will be crucial in adapting to demographic shifts and economic changes. In this way, the future of the housing market can potentially build a more accessible and equitable path to homeownership, aligning with the foundational principles of the American Dream.
Intergenerational Wealth Transfer and Its Housing Implications
The intergenerational transfer of wealth, particularly concerning housing, plays a significant role in shaping economic realities for many families. Recent studies show a stark contrast in home equity between older and younger generations, highlighting a disparity that emerges primarily from the rising costs of homeownership. As older generations accumulate substantial equity in their homes, younger individuals frequently struggle to enter the market, furthering economic inequality. This dynamic creates a scenario where the wealth gap based on homeownership widens, leading to long-term socio-economic implications.
The implications of this wealth transfer extend beyond just financial metrics; they affect community stability, access to education, and overall quality of life. Younger generations may find themselves at a disadvantage, unable to leverage home equity for investments in education or entrepreneurship, which are critical for advancing socio-economic mobility. Addressing this issue requires comprehensive policy reforms that not only tackle housing market supply and demand but also promote equitable access to homeownership for all, enabling a fair chance for economic participation and wealth building.
Strategies to Enhance Housing Accessibility
In order to tackle housing affordability and enhance accessibility, it is vital to pursue a multifaceted approach to policy reform. First and foremost, revisiting land-use regulations can pave the way for increased housing supply. Streamlining zoning processes and allowing for higher-density developments can help accommodate a growing population while maintaining community character. Moreover, incentivizing builders to undertake larger projects would align with the need for economy of scale, thereby reducing costs per unit and ultimately benefiting consumers.
Additionally, innovative financing models can also play a crucial role in bridging the affordability gap. Introducing shared equity programs or community land trusts can provide prospective homeowners with alternative pathways to ownership. These models can prevent speculative investments that drive prices up, while still allowing families to invest in and benefit from their communities. By focusing on accessibility strategies that blend regulatory reform with innovative financing, we can begin to restore the foundational dream of homeownership for a greater number of Americans.
The Role of Public Policy in Shaping Housing Outcomes
Public policy is central to shaping housing outcomes, and its role cannot be overstated when addressing the current affordability crisis. Policymakers must strike a balance between community interests and the urgent need for housing development. Effective policy should prioritize not only the frequency of new construction but also the types of housing being developed, ensuring they meet the needs of diverse populations. This could involve policies that incentivize the construction of affordable housing units and support the development of mixed-income communities that promote inclusivity.
Moreover, public investment in infrastructure and transportation can also influence housing outcomes. By improving accessibility to job markets and essential services, we can support sustainable developments in previously underutilized areas. As urban centers expand, integrating affordable housing into public transit frameworks will ensure that economic opportunities are within reach of all residents. Policymakers need to collaborate with local communities to craft comprehensive housing strategies that promote equity and resilience, ultimately leading to better outcomes in the housing market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the housing affordability crisis and how does it relate to land-use regulations?
The housing affordability crisis refers to the increasing difficulty for many Americans to afford homeownership due to rising prices. Land-use regulations, often influenced by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies, restrict the development of new housing projects. These regulations limit the number and scale of homes that can be built, contributing significantly to the affordability crisis by driving up costs and stifling construction productivity.
How do NIMBY policies exacerbate the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY policies, which reflect residents’ opposition to new housing developments in their neighborhoods, create barriers to construction. This leads to stricter land-use regulations that inhibit mass production of homes, thus increasing prices and intensifying the housing affordability crisis. As a result, fewer homes are built, and those that are tend to be customized at higher costs.
What role does construction productivity play in the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity directly impacts the housing affordability crisis by determining how efficiently homes are built. Declining productivity in construction, attributed to restrictive land-use regulations, has led to fewer homes being produced at higher costs. As a result, homeownership becomes increasingly unattainable for many, intensifying the overall crisis.
Why has homeownership become a significant challenge in the context of the housing affordability crisis?
Homeownership has become a significant challenge due to skyrocketing home prices driven by a combination of construction costs and insufficient housing supply, influenced by land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. These factors limit the availability of affordable homes, making it difficult for many to enter the housing market.
In what ways can addressing land-use regulations help alleviate the housing affordability crisis?
Addressing land-use regulations can help alleviate the housing affordability crisis by allowing for larger, more efficient construction projects. This can lead to increased housing supply, lower construction costs, and ultimately, more affordable homes for buyers. By reducing the restrictions imposed by NIMBYism, we can enhance construction productivity and make homeownership more accessible.
How can innovation in the construction sector help solve the housing affordability crisis?
Innovation in the construction sector can significantly help solve the housing affordability crisis by promoting advancements in building methods, materials, and design. Increased innovation leads to better construction productivity, allowing for more homes to be built efficiently. This can counteract the effects of NIMBY policies and land-use regulations that have historically restricted housing development.
What historical trends indicate the relationship between construction productivity and housing affordability?
Historically, construction productivity improved significantly from 1935 to 1970, coinciding with lower housing costs. However, productivity stagnated post-1970 as land-use regulations and NIMBY policies increased, directly contributing to the rise in housing prices, thereby exacerbating the housing affordability crisis that we see today.
How do housing market dynamics influence the affordability crisis?
Housing market dynamics, including supply and demand, have a profound influence on the affordability crisis. Limiting supply through strict land-use regulations and NIMBY policies leads to increased competition for available homes, driving up prices. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective solutions to enhance affordability in the housing market.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | Homeownership is increasingly out of reach for Americans, exacerbated by rising housing costs. |
| Rising Costs of Housing | The price of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960. |
| Impact of NIMBYism | NIMBY land-use policies restrict builders and hinder mass production of homes. |
| Declining Productivity in Construction | Productivity in construction fell by 40% between 1970 and 2000, contrasting with the growth in other sectors. |
| Small-scale Projects | Large-scale construction, which typically allows for greater productivity, has been decreasing. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are experiencing significant declines in housing wealth compared to older generations. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a significant issue affecting many Americans today. Rising housing costs have outpaced wage growth and have made homeownership unattainable for a growing number of individuals and families. Factors such as restrictive land-use policies and declining productivity within the construction sector are contributing to this crisis, leading to smaller projects and increased prices. As a result, there is a stark contrast between the housing wealth of older versus younger generations, highlighting an urgent need for reform in housing policies to enhance affordability and accessibility in the market.