In a rapidly changing landscape where traditional job security is fading, entrepreneurialism and work have taken center stage as individuals redefine their professional identities. This shift towards self-employment and freelancing has created opportunities for many to make their own job, allowing for greater flexibility and autonomy. An entrepreneurial mindset is essential, empowering people to harness their skills and creativity in an increasingly freelance work culture. The rise of various entrepreneurial roles, such as solopreneurs and sidepreneurs, demonstrates the diverse ways in which people engage with work today. Therefore, understanding the implications of entrepreneurialism on our professional lives is crucial as we navigate this evolving economy.
As the nature of work continues to evolve, terms like self-employment and freelancing are becoming synonymous with modern job creation. The traditional work paradigm is shifting, leading individuals to adopt a more pro-active approach to their careers by crafting their own roles. This transformation has incentivized many to explore opportunities beyond standard employment, fostering a vibrant work culture centered around creativity and initiative. Embracing an entrepreneurial spirit not only fuels personal ambition but also reshapes how we perceive professional success in the 21st century. This discussion around new forms of work invites us to rethink our relationship with career fulfillment and the broader implications of an entrepreneurial society.
The Rise of Entrepreneurialism in American Work Culture
In recent decades, the landscape of work culture in the United States has undergone a profound transformation, largely characterized by the rise of entrepreneurialism. This paradigm shift has seen the emergence of various forms of self-employment, ranging from freelancers to gig economy participants. The term ‘entrepreneurialism’ encapsulates not just those who own a business, but also those who adopt an entrepreneurial mindset within the confines of their employment—employees reshaping their roles to apply their unique skills and creativity. This democratization of entrepreneurship allows individuals to redefine their careers and take ownership of their professional paths.
Erik Baker’s book “Make Your Own Job” delves into this evolution by tracing back to the industrial era and the structural changes that have reshaped American work. He highlights how technological advances led to job losses and prompted individuals to embrace a new work ethic centered around creating one’s own opportunities. In this sense, work culture has evolved to foster an environment where self-employment is not just a choice but a necessity for many, with people feeling compelled to innovate tirelessly to thrive.
The Entrepreneurial Mindset: Thriving in the Gig Economy
The concept of the entrepreneurial mindset transcends traditional notions of self-employment and freelancing. It represents a way of thinking that emphasizes creativity, resilience, and the ability to adapt to constantly changing environments. As more individuals turn to gig work and freelancing as their primary sources of income, cultivating an entrepreneurial mindset becomes crucial for success. This mindset empowers individuals to approach challenges as opportunities and encourages lifelong learning and adaptation, which are vital in the fast-paced gig economy.
Within this framework, individuals who adopt an entrepreneurial spirit can leverage their unique skills to carve out niches in their respective markets. For instance, freelance workers today can find success by identifying specific needs in the market and tailoring their services accordingly. This approach not only enhances job satisfaction but also aligns with the broader idea of making one’s own job, where traditional corporate structures are redefined to suit personal ambitions and lifestyle preferences.
Navigating the Challenges of Freelancing
While the allure of freelancing and self-employment presents numerous benefits, such as flexibility and autonomy, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Freelancers often face uncertainty regarding income stability and lack traditional employment benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. This precarious nature of freelancing can result in heightened anxiety and stress, leading many to question if they can sustain this lifestyle long-term. As Baker points out, the fear of failure looms large in entrepreneurialism, making it difficult for many to relax and enjoy the fruits of their labor.
Moreover, the demand for self-discipline and self-promotion places significant pressure on freelancers to continuously market their skills and secure new clients. In an environment where competition is fierce, understanding how to effectively promote oneself becomes imperative. This necessity can often deter individuals from pursuing freelancing altogether, even though it offers a path to personal and professional fulfillment. Navigating these challenges requires not only an entrepreneurial mindset but also robust strategies for financial management and client acquisition.
The Impact of Technology on Self-Employment Trends
Technological advancements have dramatically reshaped the landscape of self-employment and freelancing. With the rise of digital platforms, it has become easier than ever for individuals to start their own businesses or offer freelance services. Platforms such as Upwork and Fiverr connect freelancers with clients worldwide, reducing geographical barriers and opening up an array of opportunities. This accessibility has contributed to the growing trend of self-employment, where individuals can leverage technology to create and market their own jobs in ways that were previously unimaginable.
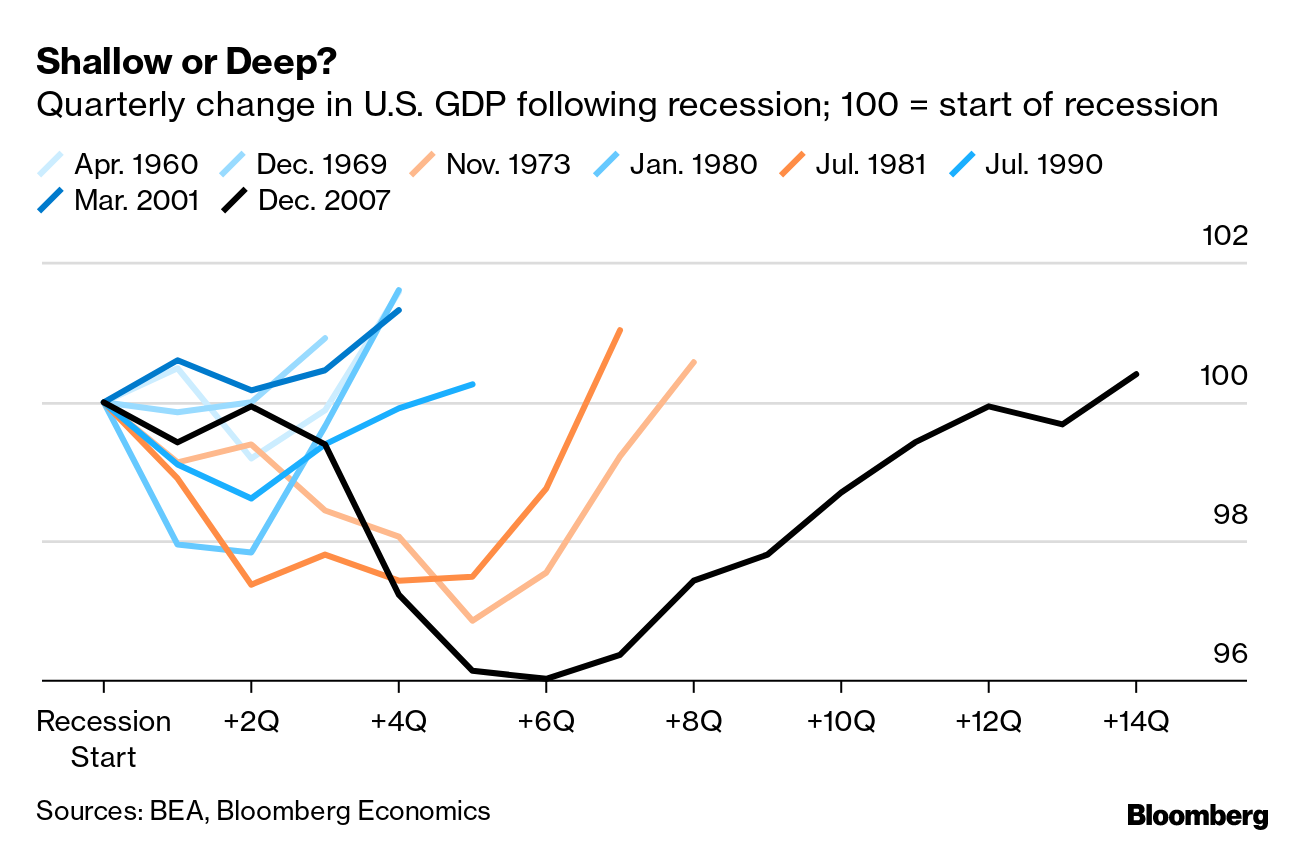
However, as Baker points out, the growth of technology also entails increased competition and the potential for job displacement. Many entrepreneurs find themselves in a race against not only their peers but also automation and AI advancements that threaten traditional job roles. Thus, the relationship between technology and work culture is complex; while it enables entrepreneurial opportunities, it also requires individuals to continually adapt their skills to remain relevant in an ever-evolving job market.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Work Ethic in America
Understanding the historical context of work ethic in America sheds light on why entrepreneurialism has gained such traction. Baker traces the roots of this shift back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when industrialization led to significant economic changes and resulting job losses. As traditional employment opportunities dwindled, Americans began to embrace the concept of ‘making your own job’—a notion that resonated deeply with the personal aspirations and ambitions of the time.
With this shift came a new work ethic that emphasized personal responsibility, creativity, and self-initiative. Throughout the decades, narratives in self-help literature have reinforced these ideals, encouraging Americans to view their work as an avenue for personal fulfillment. The rise of entrepreneurialism was therefore not just a response to economic pressures but also a cultural evolution reflecting changing attitudes towards work and self-identity.
The Psychological Toll of Entrepreneurialism
The psychological implications of entrepreneurialism are significant and often overlooked. Baker highlights that the pressure to constantly innovate and succeed can lead to feelings of inadequacy and burnout among those trying to ‘make their own jobs.’ The cultural glorification of success in entrepreneurial ventures often disregards the harsh realities and emotional toll associated with such pursuits. This relentless pursuit of achievement creates a paradox where individuals feel compelled to work harder yet struggle to find fulfillment in their efforts.
Additionally, as more people engage in entrepreneurial activities, the societal expectations surrounding success and productivity intensify. Many find themselves in a constant state of anxiety about their performance and the fear of failure, which can overshadow the joy of creating something unique. Recognizing and addressing these psychological challenges is essential for sustaining a healthy relationship with work, suggesting a need for a broader understanding of what it means to succeed in this new work culture.
The Role of Self-Help Literature in Shaping Entrepreneurial Spirits
Self-help literature has played a pivotal role in shaping the entrepreneurial spirits of many Americans. Authors like Napoleon Hill and later figures in the self-improvement genre have championed the idea of turning one’s passion or skills into a business venture. The ongoing popularity of such literature reflects a cultural shift towards valuing independence and self-sufficiency in one’s career pursuits, motivating readers to take control of their professional destinies.
These texts often provide frameworks and guidelines for cultivating an entrepreneurial mindset, emphasizing the importance of persistence, creativity, and networking. As people read and resonate with the advice in these works, they are inspired to take actionable steps toward self-employment and to embrace the challenges that come with it. This growing reliance on self-help resources indicates a cultural alignment towards entrepreneurialism that is both proactive and reflective of the evolving economy.
Strategies for Success in Self-Employment
Embracing self-employment requires strategic planning to ensure sustainable success. Setting clear goals, building a robust network of clients, and continuously developing skills are all vital components for freelancers and entrepreneurs alike. These strategies involve not only marketing one’s services but also understanding market trends and client needs, which can significantly influence one’s ability to thrive in a competitive landscape.
Moreover, fostering a balanced work-life dynamic is crucial for maintaining motivation and preventing burnout. While the allure of always being available is strong in entrepreneurial environments, it is essential to establish boundaries that allow time for personal well-being. Creating a schedule that promotes productivity while allowing for breaks and personal time can lead to greater satisfaction and long-term success in self-employment.
The Future of Entrepreneurialism in a Changing Economy
As we move deeper into the 21st century, the future of entrepreneurialism appears both promising and daunting. The rise of automation and artificial intelligence poses challenges that require a rethinking of traditional employment models. Those engaged in entrepreneurial activities may need to adapt their strategies continuously to stay ahead of technological advancements affecting their industries. This adaptability will be crucial for entrepreneurs looking to thrive in increasingly competitive markets.
However, the foundational principles of entrepreneurialism—innovation, resilience, and self-motivation—will likely remain relevant. Individuals who can harness these attributes while remaining adaptable are poised to succeed in the face of uncertainty. As the economy continues to evolve, the entrepreneurial spirit may well become the defining characteristic of the modern workforce, emphasizing the importance of not only making your own job but also redefining what work means to each individual.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the entrepreneurial mindset and how does it relate to self-employment?
The entrepreneurial mindset is a way of thinking that embraces innovation, risk-taking, and resilience in pursuing opportunities. It relates to self-employment as individuals with this mindset are more likely to engage in self-employment or freelancing, leveraging their unique skills to create and sustain their own ventures. They view challenges as opportunities for growth, making self-employment a natural extension of their entrepreneurial spirit.
How does freelancing contribute to the evolving work culture in the modern economy?
Freelancing plays a significant role in the evolving work culture by promoting flexibility, autonomy, and a project-based approach to work. As more individuals opt for freelance careers, it challenges traditional employment structures and encourages businesses to adapt to a workforce that values independence and diverse skill sets. This shift enhances the entrepreneurial ecosystem, allowing individuals to ‘make their own job’, fostering innovation and creativity.
What challenges do freelancers face in the current work environment?
Freelancers face several challenges, including income instability, lack of benefits, and the need for self-discipline. Additionally, they often grapple with building a client base and managing their own marketing, which can be daunting without the support of a traditional employment structure. These challenges highlight the importance of an entrepreneurial mindset, as freelancers must continuously adapt and innovate to thrive in a competitive market.
What historical factors influenced the rise of entrepreneurialism and self-employment in America?
Historical factors influencing the rise of entrepreneurialism in America include significant economic shifts, such as the decline of manufacturing jobs during the late 19th to early 20th century, leading to increased unemployment and the necessity for individuals to create their own opportunities. The cultural emphasis on individualism and self-promotion, especially during times of economic stress, further fueled the growth of self-employment and the entrepreneurial spirit in the nation.
How can individuals develop an entrepreneurial mindset for better career opportunities?
Individuals can develop an entrepreneurial mindset by embracing continuous learning, being open to risk, and cultivating creativity in problem-solving. Engaging in networking, seeking mentorship, and actively pursuing self-employment or freelance opportunities can enhance this mindset. Additionally, adopting a growth-oriented attitude and being resilient in the face of challenges will equip individuals to seize opportunities and navigate the modern work landscape effectively.
What impact does the gig economy have on traditional work structures?
The gig economy significantly impacts traditional work structures by providing alternative employment pathways that prioritize flexibility and independence. This paradigm shift encourages businesses to rethink workforce management and adapt to freelance and temporary roles as viable solutions to meet dynamic market demands. As more individuals turn to gig work, the necessity for traditional roles diminishes, prompting a reevaluation of work culture and employment expectations.
What is ‘make your own job’ and how does it embody entrepreneurialism?
‘Make your own job’ is a concept that encourages individuals to create personal employment opportunities that align with their skills and passions, embodying the core principles of entrepreneurialism. This approach shifts the focus from seeking traditional employment to actively pursuing self-employment or freelance work, promoting innovation, self-management, and the development of unique services or products in the marketplace.
How does entrepreneurialism affect work-life balance in today’s economy?
Entrepreneurialism often blurs the lines between work and personal life, as individuals take on the responsibility of their own success. While this can lead to fulfilling work experiences, it may also result in challenges maintaining work-life balance, as the pressure to succeed can create stress and anxiety. Developing time management skills and setting boundaries is crucial for entrepreneurs and freelancers to maintain a healthy work-life balance amidst the demands of their careers.
In what ways can managers adopt an entrepreneurial mindset to enhance team performance?
Managers can adopt an entrepreneurial mindset by fostering a culture of creativity, innovation, and collaboration within their teams. Encouraging employees to take ownership of their projects, promoting open communication, and supporting risk-taking can empower teams to exceed expectations. By treating employees as valuable contributors rather than subordinates, managers can inspire greater engagement and initiative, improving overall team performance.
How can aspiring entrepreneurs identify viable self-employment opportunities?
Aspiring entrepreneurs can identify viable self-employment opportunities by assessing market needs, leveraging their unique skills, and exploring unmet demands within their communities. Conducting market research, networking with experienced freelancers, and experimenting with small projects can provide insights into potential niches. Additionally, staying informed about industry trends will help aspiring entrepreneurs pinpoint opportunities where they can apply their expertise effectively.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The rise of entrepreneurialism reflects a shift in Americans’ relationship with work, emphasizing individualism and personal worth. |
| Entrepreneurialism is not limited to founders; it includes diverse roles such as managers, freelancers, and influencers. |
| Historical shifts from the late 19th century show increasing recognition of entrepreneurs amid job loss due to structural changes in industries. |
| Self-help literature has played a vital role in promoting the concept of making one’s own job and pursuing fulfillment through work. |
| During economic challenges, entrepreneurial roles, such as freelance work, gained popularity, especially among marginalized groups. |
| Modern entrepreneurialism pervades various sectors, influencing perceptions of meaningful work and personal identity. |
| Constant pressure and the fear of failure contribute to a culture of anxiety among individuals identifying as entrepreneurs. |
Summary
Entrepreneurialism and Work have evolved dramatically, highlighting a significant transformation in the American workforce. As more individuals transition into roles that define themselves as entrepreneurs, the relationship with work becomes increasingly intertwined with personal identity and purpose. This shift emphasizes ambition and the desire for meaningful engagement but also creates a culture of anxiety as individuals grapple with the inherent risks of self-employment. The embrace of entrepreneurialism not only reflects changing job landscapes but also challenges conventional views of success and fulfillment in the modern economy.